Diabetes in China
- China has the largest number of people with diabetes in the world, according to a new study conducted by the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) and Chinese Diabetes Society (CDS). This figure is twice as many people with diabetes than previously estimated.1 The prevalence however, varies by age and body mass index (BMI).
- The age-standardized prevalences of total diabetes (which included both previously diagnosed diabetes and previously undiagnosed diabetes) and prediabetes were 10% (11% among men and 9% among women) and 16% (16% among men and 15% among women), respectively. In terms of absolute numbers, 92 million adults have diabetes and 148 million adults have prediabetes.1
- The prevalence of diabetes increased from 1% in 1980 to 10% in 2008 in China which underscores the importance of socioeconomic changes in the country.2 A similar phenomenon is occurring in India where the prevalence has increased as high as 20% in some parts (See Diabetes India).3
- Especially alarming is the finding that the majority of cases of diabetes (61%) are undiagnosed and untreated.1 This may be equally true for India and other low and middle income countries (LMICs).
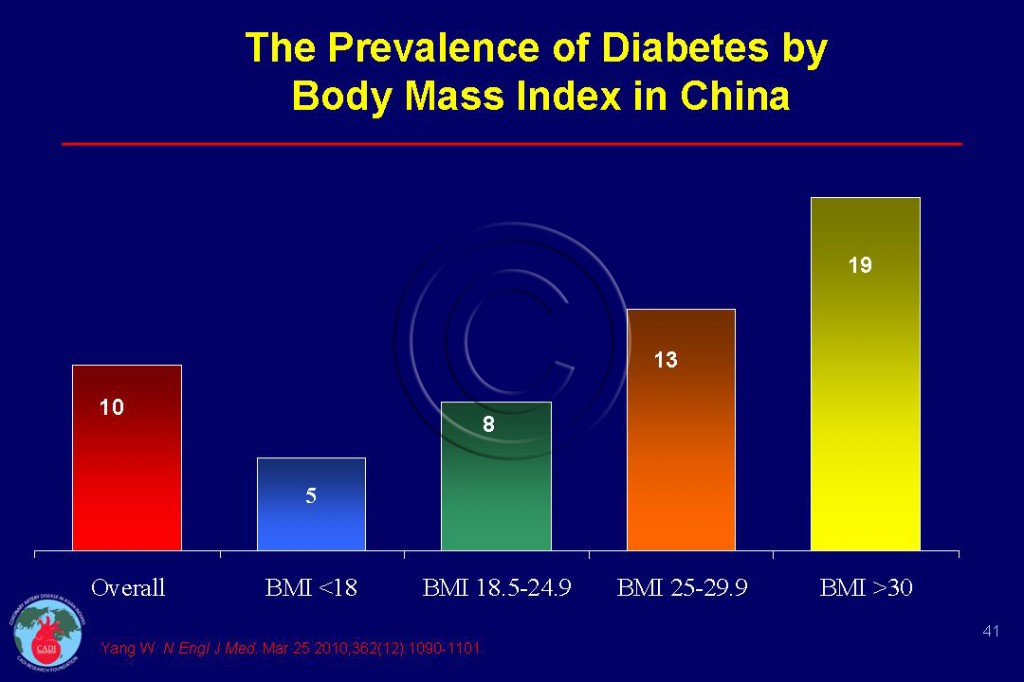
- The prevalence of diabetes is 3% and prediabetes 9% at age 20 which increases 20% and 25% respectively by 60 years of age. Likewise the prevalence of diabetes increases from a low of 5% for BMI <18, to 19 % at BMI >30 as shown in Figure 041.1
- The CDS and IDF estimate that 13% of total medical expenditures in China are directly caused by diabetes (RMB 173 billion or US $25 billion). People with diabetes in China report 3 to 4 times more in-patient care, out-patient visits, and emergency room visits than people without diabetes of the same age and sex.
- The economic burden will increase rapidly over the next 10 to 20 years when approximately 50 million Chinese with undiagnosed diabetes enter medical care, in addition to the 50 million who are already diagnosed and are receiving care. Preventable diabetic complications such as stroke, blindness, and kidney disease would further double or triple the medical expenditure.
- Strikingly, the health expenditure increased dramatically with the duration of diabetes. For example, the health expenditure for Chinese who have had diabetes for 10 or more years are 460% higher than for people who have had diabetes for less than 2 years.
- People are getting diabetes at a younger age and at a lower BMI. However, China has a window of opportunity to prevent an epidemic of serious diabetes complications, which will decrease the health spending dramatically.
- Currently, fewer than 5% of Chinese people with diabetes have experienced stroke, heart attack, and/or heart failure. Less than 5% report kidney disease, eye surgery, or problems with their feet or legs.
- Half the people interviewed use glucose-lowering drugs but few use anti-hypertensives (16%), statins (1%), or aspirin (13%), which are inexpensive, highly effective, and together can lower the risk of complications by 50% or more.
- More than half of Chinese men with diabetes are smokers. Since smoking doubles the risk of diabetes complications, quitting cigarettes is another effective strategy of preventing complications.
- The Chinese Ministry of Health has introduced large-scale diabetes awareness and education programs to address diabetes, driven by the CDS.
- These findings are further proof that diabetes represents a major barrier to development in low and middle-income countries, as well as emerging economic powerhouses such as India.
Sources
1. Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med. Mar 25 2010;362(12):1090-1101.
2. Hu FB. Globalization of Diabetes: The role of diet, lifestyle, and genes. Diabetes Care. Jun 2011;34(6):1249-1257.
3. Ramachandran A, Mary S, Yamuna A, Murugesan N, Snehalatha C. High prevalence of diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors associated with urbanization in India. Diabetes Care. May 2008;31(5):893-898.